
Go to Survivor Mall.com
Defending the Faith, Evangelizing the Eschaton
Here is the trailer for the soon to be released film I was interviewed for: The Last Pope?
I affirm Ryrie’s second point the basic dispensational philosophy of history as well. A philosophy of history is a systematic understanding in which past events and major sequences are unified and explained in light of a future ultimate meaning.[i] While all Christians believe the ultimate meaning is found in Christ, they disagree in the form and function. Paul wrote to the church in Ephesus, “To me, though I am the very least of all the saints, this grace was given, to preach to the Gentiles the unsearchable riches of Christ, and to bring to light for everyone what is the plan of the mystery hidden for ages in God who created all things,” (Eph 3:8–9, underline added). “The plan” is a rendering of the Greek οἰκονομία meaning “a plan which involves a set of arrangements (referring in the NT to God’s plan for bringing salvation to mankind within the course of history)—‘purpose, scheme, plan, arrangement.’”[ii]
In the second century, Irenaeus wrote, “He who, by Moses, instituted the legal dispensation, by which giving of the law we know that He spake to the fathers.”[iii] He then divides biblical history based on “four principal (καθολικαί) covenants given to the human race.”[iv] In the third century, church father Tertullian used the Latin word dispensatio to translate οἰκονομία and from that the English word dispensation derives. Hence, used in this way, a dispensation refers to a distinctive way in which God administers His relationship with mankind. As one can see, this line of thinking was present in primitive Christianity. In this way, nineteenth century dispensationalists were actually recovering theology that had been lost under centuries of Roman Catholic oppression.
As a system, dispensationalism has the most coherent philosophy of history because it accounts for the whole range of predictive prophecy. For example, the Old Testament predicts an earthly kingdom of universal peace (Is 2:2-4, 11:6-9, 65:17-25; Mic 4:1-5). Accordingly, futurist premillennialism accounts for the biblical data affirming that Christ will return to earth and rule over it for 1,000 years (Rev 20:4). Even so, I am willing to allow that “χίλια ἔτη” could be an idiom for a long period of time rather than insisting on precisely one thousand years. I agree with earlier divisions including the Adamic and Noahic dispensations found in revised dispensationalism. I somewhat appreciate the simplicity of the simple four-part structure associated with progressive dispensationalism: 1) Patriarchal (creation to Sinai); 2) Mosaic (Moses to Jesus ascension); 3) Ecclesial (ascension to second coming), and 4) Zionic (the millennial kingdom and eternal new creation).[v] However, Ryrie argues that progressive dispensationalists make the goal atemporal by conflating eternity and the millennium.[vi] While progressives place the millennial reign prior to the eternal state within the Zionic dispensation, it seems to confuse the matter. Thus, I agree with the older school that posits the eternal state as a distinct unit. Hence, my position entails: 1) Adamic; 2) Noahic; 3) Patriarchal; 4) Mosaic; 5) Church; 6) Millennial; 7) Eternal. These offer more explanatory scope than the abridged scheme presented by progressives. Ultimately, the exact number and name of the dispensations is not as important as one’s hermeneutic.
On the third point, a literal interpretation of scripture, I think the work of progressive dispensationalists is helpful. Literal interpretation needs to be informed by literary understanding (e.g. genre). While the historical grammatical hermeneutic is best, biblical scholarship is certainly more informed today than the days of Darby and Scofield. The radical bifurcation of the church and Israel advocated in classic dispensationalism goes too far. Classic dispensationalists posited the Church and Israel as eternally separate. The Rose Guide to End Time Prophecy is helpful:
- Classic dispensationalists see the church as God’s heavenly people and Israel as God’s earthly people. These two groups will remain separate even in eternity. The church will be in heaven. Israel will be on the earth. (John Nelson Darby, Lewis Sperry Chafer, Cyrus I. Scofield)
- Revised dispensationalists still see the church and Israel as distinct. At the same time, they expect the saved from both groups to coexist in eternity in glorified and resurrected bodies. Ethnic Israel is the physical seed of Abraham; prior to the end of time, the nation of Israel will still receive the land that God promised. God temporarily set aside the unbelieving nation of Israel so that he could bring together believing Gentiles with a remnant of believing Jews in the church. The church is the spiritual seed of Abraham and includes believing Jews and Gentiles. (John Walvoord, Charles Caldwell Ryrie, J. Dwight Pentecost)
- Progressive dispensationalists are similar in many ways to new covenantalists. According to progressive dispensationalists, God has had one plan that he has unfolded from the beginning of time to the present. Each dispensation has simply emphasized a different aspect of this one plan. Jesus inaugurated a kingdom during his earthly ministry, and he will bring this kingdom to fruition in a future millennium. The nation of Israel will still receive the land that God promised to Abraham, and Jesus will govern Jews and Gentiles according to their separate nationalities during the millennium. The plan of God will, however, ultimately culminate with one people, joined together in the presence of God for all eternity.(Craig Blaising, Darrell Bock, Bruce Ware)[vii]
Even given classic’s extremes, they served as a needed corrective. Theology Professor at LBTS, Dan Mitchell cogently qualifies the final point, “It’s not so much the idea of a literal interpretation that marks the distinction, but it is the approach, do you approach the text inductively from Genesis forward or deductively from the fulfillment backward. If you have already decided that everything is fulfilled in Christ, then there really isn’t much to talk about in terms of future eschatology.”[viii] For these reasons, I believe the dispensationalism is superior to covenant theology and I find myself somewhere in the tension between the progressive and revised schools of thought.
This essay offered an analysis of dispensationalism. It sought to illustrate the value of the system by examining three defining points: the distinction between the church and Israel, the philosophy of history and a literal hermeneutic. The relationship between these points was shown. In the end, it seems that these points support the idea that dispensationalism is the key to biblical prophecy.
[i] Renald E. Showers, There Really Is a Difference! : A Comparison of Covenant and Dispensational Theology (Bellmawr, NJ: The Friends of Israel Gospel Ministry, 1990). 22.
[v] Craig A. Blaising and Darrell L. Bock, Progressive Dispensationalism (Grand Rapids, MI: Baker Books, 1993), 123.
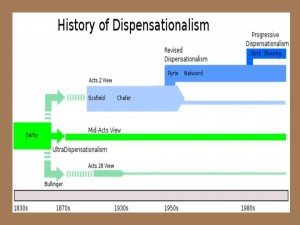 Arguably from the inception of the church (although lost under Romanism), dispensationalism has been and still is the key to biblical prophecy. Since its recovery in the nineteenth century there have been three major versions: classic (Darby, Larkin and Scofield), revised (Walvoord, Pentecost, Chafer, and Towns), and progressive (Bock, Blaising, Feinberg and Saucy) dispensationalism. All divide history based on God’s covenants as successive revelations in the progression of God’s redemptive program and sustain a premillennial futurist interpretation of prophecy. As a founding member of the revised school, Charles Ryrie emphasized three elements: 1) Distinction between church and Israel;[i] 2) Philosophy of History;[ii] 3) Literal interpretation of scripture.[iii] He offers strong and compelling arguments against covenant theology which is the system of theology that centers on two contrived covenants: the covenant of works and the covenant of grace.[iv] It typically dismisses God’s actual covenant promises to Israel and argues that most all of prophecy is fulfilled in Christ. While I’m largely in agreement with Ryrie that covenant theology is an artificial system lacking biblical support, I do think progressive dispensationalists make some good points.
Arguably from the inception of the church (although lost under Romanism), dispensationalism has been and still is the key to biblical prophecy. Since its recovery in the nineteenth century there have been three major versions: classic (Darby, Larkin and Scofield), revised (Walvoord, Pentecost, Chafer, and Towns), and progressive (Bock, Blaising, Feinberg and Saucy) dispensationalism. All divide history based on God’s covenants as successive revelations in the progression of God’s redemptive program and sustain a premillennial futurist interpretation of prophecy. As a founding member of the revised school, Charles Ryrie emphasized three elements: 1) Distinction between church and Israel;[i] 2) Philosophy of History;[ii] 3) Literal interpretation of scripture.[iii] He offers strong and compelling arguments against covenant theology which is the system of theology that centers on two contrived covenants: the covenant of works and the covenant of grace.[iv] It typically dismisses God’s actual covenant promises to Israel and argues that most all of prophecy is fulfilled in Christ. While I’m largely in agreement with Ryrie that covenant theology is an artificial system lacking biblical support, I do think progressive dispensationalists make some good points.
Concerning point one, I strongly disagree with supercessionism (that the church has entirely superseded Israel or replacement theology). I believe God will fulfill His Old Testament promises as they were understood, not in the decontextualized manner applied to the Church found in Roman Catholicism and unfortunately most of evangelical covenant theology. In this sense, the reformers stopped short. God made specific promises to the descendants of Jacob and David concerning their ancestral line, the land and political sovereignty. Only the Mosaic covenant was conditional. The Abrahamic (Gen 12) and Davidic (2 Sam. 7) were unconditional and everlasting. The Davidic is often overlooked:
“And I will appoint a place for my people Israel and will plant them, so that they may dwell in their own place and be disturbed no more. And violent men shall afflict them no more, as formerly, from the time that I appointed judges over my people Israel. And I will give you rest from all your enemies. Moreover, the Lord declares to you that the Lord will make you a house. When your days are fulfilled and you lie down with your fathers, I will raise up your offspring after you, who shall come from your body, and I will establish his kingdom. He shall build a house for my name, and I will establish the throne of his kingdom forever. I will be to him a father, and he shall be to me a son. When he commits iniquity, I will discipline him with the rod of men, with the stripes of the sons of men, but my steadfast love will not depart from him, as I took it from Saul, whom I put away from before you. And your house and your kingdom shall be made sure forever before me. Your throne shall be established forever.’(2 Sa 7:10–17 cf. 1 Chron. 17)
Like the Abrahamic covenant, the Davidic covenant was irrevocable—“established forever” and despite innumerable acts of unfaithfulness on Israel’s part, God will be absolutely faithful. The Davidic covenant promises to Israel a political, religious, visible earthly kingdom, and God personally guaranteed that it would endure forever and that all nations would be blessed through it, based on His faithfulness.
“I have found David, my servant; with my holy oil I have anointed him, so that my hand shall be established with him; my arm also shall strengthen him. The enemy shall not outwit him; the wicked shall not humble him. I will crush his foes before him and strike down those who hate him. My faithfulness and my steadfast love shall be with him, and in my name shall his horn be exalted. I will set his hand on the sea and his right hand on the rivers. He shall cry to me, ‘You are my Father, my God, and the Rock of my salvation.’ And I will make him the firstborn, the highest of the kings of the earth. My steadfast love I will keep for him forever, and my covenant will stand firm for him. I will establish his offspring forever and his throne as the days of the heavens. If his children forsake my law and do not walk according to my rules, if they violate my statutes and do not keep my commandments, then I will punish their transgression with the rod and their iniquity with stripes, but I will not remove from him my steadfast love or be false to my faithfulness. I will not violate my covenant or alter the word that went forth from my lips. Once for all I have sworn by my holiness; I will not lie to David. His offspring shall endure forever, his throne as long as the sun before me. Like the moon it shall be established forever, a faithful witness in the skies.” Selah( Ps 89:20–37)
God spoke through the original inspired author who certainly did not have an ethereal metaphorical Israel in mind when he composed those words. David understood the promises in a matter of fact manner. I have never read a supercessionist reply to these passages that did not cast God in the role of a prankster who deceived David.
Paul writes in Romans that Gentiles are grafted into Israel. This implies God’s chosen people includes the church as well as a remnant of ethnic Israel, now and especially at the Second Coming (Rom 11:26-27, Zec 12:10). While the distinction applies in this current dispensation due to Israel’s supernatural blinding (Rom 11:25; 2 Cor 3:14; Mat 23:39), I believe we merge into one people at Christ’s return. Thus, I commend the holistic view described by Bock and Blaising, “God will save humankind in its ethnic and national plurality. But, He will bless it with the same salvation given to all without distinction; the same, not only in justification and regeneration, but also in sanctification by the indwelling Holy Spirit.”[v] It seems unlikely that ethnicity will much matter upon Christ’s return to rule from Jerusalem.
Next week part two picks up with the dispensational philosophy of history.
[i] Charles Caldwell Ryrie, Dispensationalism, (Chicago: Moody Publishers, 1995), 148.
[ii] Ryrie, Dispensationalism, 20.
[iii] Ryrie, Dispensationalism, 102.
[iv] Stanley Grenz, David Guretzki and Cherith Fee Nordling, Pocket Dictionary of Theological Terms (Downers Grove, Ill.: InterVarsity Press, 1999), 32.
Amillennial
Antichrist
Apologetics
Apostasy
Armageddon
Atheism
Bart Ehrman
Bible
Chuck Missler
Creation
creationism
Cris D. Putnam
Cris Putnam
Cults
Daniel
Day of the Lord
End Times
Eschatology
Exo-Vaticana
Faith
Heresy
Heretic
Intelligent Design
Jesus
Joseph Smith
last days
Micheal Heiser
Millennium
Mormons
Petrus Romanus
Pluralism
Premillennial
Prophecy
Rapture
Resurrection
Resurrection Challenge
Revelation
Rob Skiba
Romanism
Russ Houck
Satan
Thomas Horn
Transhumanism
Trinity
UFO Apocalyptic Literature (2)
Apologetics (194)
Archeology (5)
Bible Exposition (23)
Bioethics (1)
Book Review (3)
Charity (1)
Conference (4)
Debate (3)
Eschatology (33)
Evolution (2)
Exo Vaticana (36)
Gender (1)
Hebrew Roots Movement (3)
Homosexuality (2)
Intelligent Design (8)
Interview (7)
Islam (2)
Movie Review (1)
My Books (8)
Nation Under Judgment (2)
NDE (1)
Occult (2)
On the Path of the Immortals (6)
Petrus Romanus (49)
Product Offer (1)
Putin (1)
Roman Catholicism (2)
Roman Catholocism (3)
Science (1)
Spiritual Warfare (5)
The Final Roman Emperor (3)
The Last Roman Emperor (1)
Theology (3)
Transhumanism (6)
TV appearances (8)
Uncategorized (3)
WP Cumulus Flash tag cloud by Roy Tanck requires Flash Player 9 or better.
Copyright © 2025 · Logos Apologia
